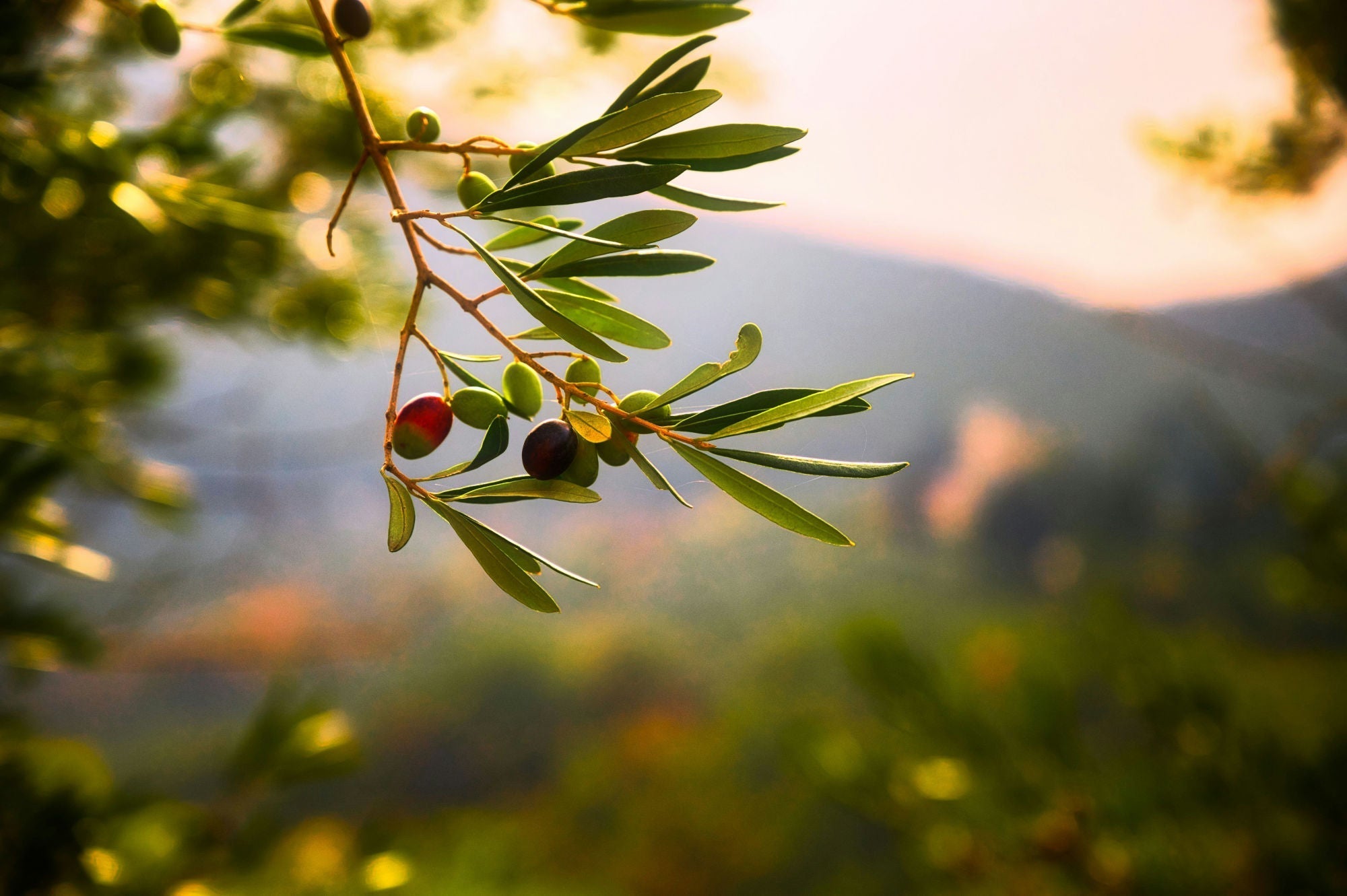
Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food! wrote the most famous doctor of antiquity, Hippocrates of Kos. Possibly the legendary medical pioneer was sitting in the shade of an old olive tree when he wrote this, and he undoubtedly knew the immense medicinal healing powers this tree possesses.
It's not about the fruits or the valuable oil, whose precious unsaturated fatty acids benefit our health. Rather, it's about the concentrated healing power contained in the leaves of the olive tree, which, rediscovered today, can be used as an extract.
Olive leaf extract – a treasure of nature with almost magical abilities
Olive leaf extract is a true all-rounder: it acts antiviral, antifungal, immune-boosting, and against parasites. Additionally, it reduces oxidative stress, inhibits inflammation, and is also antibacterial.
To understand the power contained in the leaves of the olive tree, one only needs to look at how and especially where it thrives. For example, many of the Mediterranean islands are barren, dry, hot, and barely covered with significant vegetation. Yet an ancient olive tree can almost always be found somewhere, sometimes in the most unlikely places where neither water nor nutrients are expected.
Olive trees root deeply and can live over 1000 years

In the barren landscapes where olive trees can survive, the power of these trees becomes evident. With suitable soil conditions, the roots can reach depths of up to six meters and absorb tiny amounts of water from there to nourish fruits and leaves. If left to thrive undisturbed, the olive tree can easily live for several thousand years. One of the oldest specimens stands on Crete and is probably around 5000 years old.
Besides these survival skills, the miraculous power of the olive tree is evident both in its fruits, the olives, and in the leaves it produces. The fruits are either eaten raw or processed into olive oil. Olive leaves can be brewed as tea or processed into extract. Olive leaf extract, in liquid form or as a capsule, is considered a valuable natural remedy with numerous positive effects on our health.
Olive leaves in folk medicine
In folk medicine, olive leaves have played a significant role for a long time. The ancient Romans and Greeks already knew how to treat various ailments with the leaves of the olive tree. Especially in the Mediterranean region, olive leaves had a firm place in traditional medicine.
But Hildegard of Bingen also knew the healing power of olive leaves. For example, she treated digestive system disorders with a tea made from fresh olive leaves. However, because the taste of this tea is quite astringent and slightly bitter, nowadays olive leaf extract in liquid or capsule form is more commonly used.
A distinction:

Olive leaves and the olive leaf extract derived from them affect our body completely differently than olive oil does:
-
Olive oil mainly contains valuable unsaturated fatty acids.
-
Olive leaf extract contains, among other things, many secondary plant compounds and highly concentrated polyphenols. These include substances and groups such as oleuropein, flavonoids, phytosterols, hydroxytyrosol, terpenes, and glycosides.
Health effects of olive leaf extract
The main active ingredient in olive leaf extract is the so-called oleuropein. It is a powerful antioxidant found in almost all parts of the olive tree - the root, bark, and fruit. However, oleuropein is especially present in the olive leaves. Here, the concentration is highest at nearly 950 mg per 100 ml. Some manufacturers of olive leaf extract products further concentrate this active ingredient, reaching levels of up to 2,200 mg per 100 ml.
The health benefits of olive leaf extract mainly arise from the combination of various health-promoting ingredients, which enhance each other's effectiveness through their mutual interaction. In particular, the strong antioxidant effect of olive leaf extract is also based on its high content of chlorophyll and many secondary plant compounds.
Olive leaf extract can be used for many medicinal purposes. Among other effects, it acts antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal (against fungi), antiparasitic, immune-strengthening, and anti-inflammatory.
Olive leaf extract and anti-aging
Oleuropein, the main active ingredient of olive leaf extract, is primarily supposed to protect the health of the olive tree. It protects it from damage caused by insects, bacteria, fungi, free radicals, or viruses. The high content of oleuropein strengthens the tree so much that it can live for several thousand years.
The question now is whether this enormous increase in vitality can also benefit humans. Cell studies conducted so far have already shown that olive leaf extract positively influences the lifespan of cells and supports the cells' own self-cleaning processes.
Whether taking olive leaf extract preparations can stop aging is questionable – but it is certainly not wrong to take such products preventively.
Digestive problems
Digestive complaints can have numerous causes: they sometimes arise from parasites, fungi, viruses, or bacteria. Many of these complaints also involve inflammations of the intestinal mucosa.
Here, olive leaf extract unfolds its cleansing effect. It removes foreign bacteria from the digestive tract and contributes to the regeneration of the intestinal flora. Fungal and parasitic diseases can also be positively influenced.
Bladder infections and fungal diseases
Thanks to its strong antibacterial and antifungal effect, the intake of olive leaf extract preparations is also suitable for complaints of the urinary tract and genitals. For example, those who frequently suffer from bladder problems or have vaginal yeast infections can take appropriate products.
However, it is advisable to discuss the exact intake and dosage in advance with a naturopath or a doctor specialized in natural medicine.
Colds and flu
In flu infections and colds, viruses as well as bacteria are often active in the body. Here, olive leaf extract can act against the corresponding pathogens and strengthen the immune system from within, so that an infection does not even occur. If a disease is already present, olive leaf extract can alleviate the symptoms and promote healing.
The effect of olive leaf extract on the heart and circulatory system
Diseases of the cardiovascular system are often caused by chronic inflammations that spread to the walls of the blood vessels and can cause fine injuries there. Due to these micro-injuries, deposits can form, which among other things consist of cholesterol.
This is where the anti-inflammatory effect of olive leaf extract preparations comes into play. Because if these inflammations are stopped from the start, the risk of blood vessel changes can also be reduced, which is particularly helpful for patients with an increased risk of stroke or heart attack.
Here too, it is definitely advisable to discuss any potential intake in advance with a naturopath or natural medicine doctor.
Arthritis
Because olive leaf extract has an anti-inflammatory effect and can alleviate numerous diseases and inflammations, it is assumed that its active ingredients can also be helpful in rheumatic diseases, such as arthritis. In a study conducted in 2012, it was found that olive leaf extract significantly reduced tissue changes and swelling caused by arthritis. It is therefore likely that olive leaf extract could play an important role in the future treatment of arthritis.
Protection against radioactive radiation
Various studies show that olive leaf extract can protect against cell damage caused by X-rays if the preparations are taken either before or after radiation. It is suspected that the substances contained in the extract can mitigate the effects of ionizing particles on the body and thus protect the skin somewhat from the inside against harmful UV radiation.
Olive Leaf Extract: Usage and Dosage
So far, there are only a few studies from which precise dosage recommendations can be derived. In addition, the amount of oleuropein contained in each product can vary. For this reason, one should follow the respective manufacturer's dosage instructions.
Many capsules contain 500 mg of olive leaf extract with 100 mg of oleuropein. Unless otherwise specified, up to three pieces can be taken per day. However, one should always start with a low dosage and only increase it slowly if well tolerated, observing how the body reacts. Especially when olive leaf extract is used to treat digestive problems, bladder infections, or fungal diseases, it should not be taken on an empty stomach. In any case, it is better to take the capsule or extract after a light meal.
Whether you want to strengthen your immune system or protect yourself from infections, Olive Leaf Extract from Euro Nutrador offers you an effective and natural solution. Our olive leaf extract capsules are well tolerated and safe for daily use. Each capsule contains 250 mg of extract from high-quality olive leaves, as well as 10 mg of rutin.
A dosage of 3 x 1 capsule daily before or with a meal is recommended. Please discuss the intake with your doctor or health expert.
Legal notice regarding health-related claims:
Our information is for general informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Dietary supplements do not replace a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Health-related claims about dietary supplements must comply with the Health Claims Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 and be approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). If you have health complaints or questions, please consult a doctor.
Legal notice regarding health-related claims:
Our information is for general informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Dietary supplements do not replace a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Health-related claims about dietary supplements must comply with the Health Claims Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 and be approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). If you have health complaints or questions, please consult a doctor.