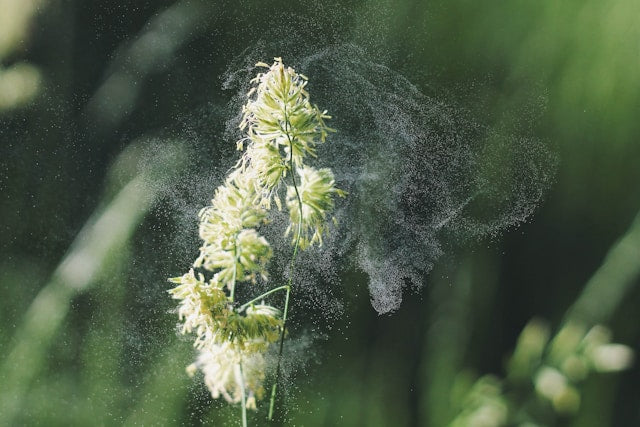
When the first delicate blossoms of the year appear, a challenging time begins for many people. Early bloomer allergies affect several million people in Germany alone and can make the start of spring a test of endurance. This article explains exactly what lies behind these allergic reactions, which symptoms are typical, and – especially important – how you can cope with natural methods and targeted Dietary supplement how you could support your immune system to better get through the allergy season.
What are early bloomer allergies?
Early bloomer allergies are among the pollen allergies (Pollinosis) and are triggered by an excessive reaction of the immune system to actually harmless pollen from early flowering plants. The most common triggers include:
-
Hazel: Flowering period from January to March
-
Alder: Flowering period from February to April
-
Birch: Flowering period from March to May
-
Ash: Flowering period from March to May
-
Elm: Flowering period from February to April
In an early bloomer allergy, the immune system mistakenly recognizes pollen proteins as dangerous intruders. It then produces specific antibodies (immunoglobulin E) that bind to mast cells in the tissue. Upon renewed contact with the allergen, these mast cells release inflammatory mediators such as histamine, which are responsible for the typical allergy symptoms.
When do early bloomer allergies occur?
The early bloomer allergy season already begins in winter and typically extends from January to April, with exact periods varying depending on weather conditions and region. In mild winters, the first allergic reactions to hazel and alder pollen can occur as early as December.
The pollen flight table provides a rough overview of the main flowering periods of the most important early bloomers:
|
Plant species |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
|
Hazel |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Alder |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Birch |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Ash |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Elm |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
For up-to-date information, it is recommended to take a look at the Pollen forecast by the German Weather Service or the use of special pollen apps that can warn you in time.
Common symptoms of early bloomer allergies
The symptoms of early bloomer allergy often resemble a cold but occur without infection and are linked to the pollen season. Typical signs include:
-
Sneezing: Frequent and sudden
-
Runny nose: Watery, clear nasal discharge
-
Itchy nose: Constant urge to rub the nose
-
Blocked nose: Difficulty breathing through the nose
-
Itchy, red eyes: Often associated with tearing
-
Itchy palate and/or throat: Scratchy throat
-
Fatigue and exhaustion: Impairment of performance
-
Coughing: Especially at night or during physical exertion
-
Headaches: Due to blocked sinuses
In particularly sensitive individuals or during intense pollen flight, the symptoms can become so severe that they significantly impair daily life and greatly reduce quality of life.
Why the body reacts allergically – and what the immune system has to do with it
The immune system is actually programmed to protect the body from harmful invaders such as viruses and bacteria. However, in an allergy to early bloomers, there is a misregulation of this protective function.
The mechanism can be explained in several steps:
-
Sensitization phase: Upon first contact with the pollen, the immune system mistakenly recognizes certain proteins as dangerous and produces specific IgE antibodies.
-
Binding of the antibodies: These IgE antibodies attach to so-called mast cells, which are mainly located in the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and airways.
-
Allergic reaction: Upon renewed contact with the pollen, they bind to the IgE antibodies on the mast cells, leading to the release of inflammatory mediators such as histamine.
-
Triggering of symptoms: Histamine and other mediators cause the typical allergy symptoms such as swelling, increased mucus production, and itching.
The immune system thus overreacts to actually harmless environmental substances, which offers no evolutionary advantage. Why some people develop allergies and others do not is not yet fully understood. Both genetic factors as well as environmental influences and modern lifestyle are discussed as possible factors.
Natural help for early pollen allergies: These active ingredients can help
Besides conventional treatments like antihistamines and cortisone, there are a number of natural substances that could have the potential to alleviate allergy symptoms and modulate the immune system. These could be considered as a complement to medical treatment.
Quercetin
Quercetin is a secondary plant compound from the flavonoid group, found in many fruits and vegetables as well as in herbs like capers and lovage. Studies suggest that quercetin could inhibit the release of histamine, by preventing mast cell degranulation.
A review article from the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology showed that quercetin has anti-inflammatory properties and could influence the allergic reaction cascade at multiple points. It could thereby contribute to relieving symptoms such as sneezing, itching, and runny nose.
Nutrador® offers high-quality dietary supplements with quercetin that could help you reduce your allergy symptoms naturally.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a well-known antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals and dampen inflammatory responses. Some studies suggest that adequate vitamin C supply could mitigate allergic reactions.
High doses of vitamin C could reduce histamine release and thus contribute to an improvement of allergic symptoms.
In combination with quercetin, vitamin C could enhance its effect by improving bioavailability and possessing anti-inflammatory properties itself.
Vitamin C is, alongside other high-quality vitamins and minerals, in the Opti Immun® capsules from Nutrador® contained.
MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)
MSM is an organic sulfur compound naturally found in various foods. Taken as a dietary supplement, MSM could support allergy symptoms by reducing the permeability of mucous membranes, thereby decreasing contact with allergens.
Research findings suggest that MSM could modulate cytokine production and reduce oxidative stress. A clinical study in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine showed that MSM supplementation could significantly improve symptoms of seasonal allergies.
Nutrador® offers high-quality MSM products, which could contribute to supporting your mucous membrane health and allergy management.
Spirulina
Spirulina is a nutrient-rich blue-green algae known for its high protein content and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that spirulina could influence the production of immune cells and alleviate allergic reactions.
Regular intake of spirulina could lead to a significant improvement in symptoms in people with allergic rhinitis.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, have anti-inflammatory properties and could modulate the excessive immune reaction in allergies. They are mainly found in fatty fish, algae oil, and flaxseed.
Research findings suggest that adequate supply of omega-3 fatty acids could reduce the risk of allergies and lessen the severity of symptoms. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed that regular intake of omega-3 supplements could reduce the production of pro-inflammatory substances.
The high-quality Omega-3 products from Nutrador® are derived from sustainable sources and could help you relieve your allergic symptoms.
Probiotics
The gut flora plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system. Probiotics – live microorganisms such as lactobacilli and bifidobacteria – could modulate the immune response and alleviate allergic reactions by influencing the gut flora.
A meta-analysis in the World Journal of Gastroenterology showed that certain probiotic strains that could improve symptoms of seasonal allergies, by promoting the balance of the immune system and influencing the production of antibodies.
Nutrador® offers specially developed probiotics that could specifically contribute to supporting the immune system in allergies and belong to the best supplements are counted in the area of natural immune support.
Nutrition & everyday tips for pollen allergies
In addition to the targeted intake of dietary supplements, there are numerous measures in everyday life and nutrition that can help you reduce the burden of early bloomer allergies.
Everyday tips for pollen reduction
-
Optimize air filtration:
-
Keep windows closed especially in the morning hours when pollen concentration is highest
-
Use air purifiers with HEPA filters in living and sleeping areas
-
Use pollen protection screens for windows as an additional barrier
-
Hygiene measures after being outdoors:
-
Wash your hair before going to bed to remove pollen
-
Change your clothes after coming home and do not store "outerwear" in the bedroom
-
Rinse your nose with isotonic saline solution during severe symptoms
-
Minimize pollen exposure:
-
Follow the daily pollen forecast and plan activities accordingly
-
Wear sunglasses during high pollen exposure to protect your eyes
-
Avoid drying laundry outdoors during pollen season
-
Living space design:
-
Vacuum regularly with a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter
-
Wipe surfaces damp instead of dusting dry
-
Avoid carpets in favor of easily cleanable flooring
Dietary recommendations for early blooming allergies
An anti-allergic diet could relieve your symptoms and enhance the effect of natural supplements:
-
Increase anti-inflammatory foods:
-
Berries like blueberries, blackberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants
-
Leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and chard provide important vitamins and minerals
-
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and herring provide valuable omega-3 fatty acids
-
Turmeric and ginger have strong anti-inflammatory properties
-
Reduce histamine-rich foods:
-
Fermented products like aged cheese, sauerkraut, and wine
-
Certain types of fish, especially if not very fresh anymore
-
Tomatoes, spinach, and eggplants can worsen symptoms in sensitive individuals
-
Integrate immune system-strengthening foods:
-
Garlic and onions contain quercetin and sulfur-containing compounds
-
Citrus fruits offer vitamin C and flavonoids
-
Nuts and seeds provide zinc, selenium, and healthy fats
The combination of conscious nutrition and targeted Immune system supplements could help you better endure the allergy season and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion - Early bloomers, what to do?
Early bloomer allergies can make the beginning of spring a stressful time, but with the right knowledge and a combined strategy of natural active ingredients, conscious nutrition, and practical everyday measures, you could significantly alleviate your symptoms.
The various products offered by Nutrador® Nutraceuticals could be a valuable addition to your personal allergy management strategy. Especially quercetin, MSM, spirulina, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics show promising results and could help modulate your immune system and reduce allergic reactions.
However, remember that every person responds individually to different measures and it is important to listen to your body. In case of severe allergic reactions or uncertainties, you should always seek medical advice. A holistic approach that includes both conventional and natural methods often promises the best results for a symptom-free spring.
FAQ
When does the early bloomer allergy season start?
The early bloomer allergy season typically begins between January and February depending on weather and region, with the flowering of hazel and alder. In mild winters, first allergic reactions can occur as early as December. The main season extends until April/May, when birch reaches its peak bloom.
Can I combine natural remedies with antihistamines?
In principle, natural remedies like quercetin, MSM, or spirulina could be taken in addition to conventional antihistamines. However, since interactions can never be completely ruled out, it is advisable to consult medical professionals before combining them, especially if you regularly take medications.
Does quercetin really help against allergies?
Studies suggest that quercetin might inhibit the release of histamine by preventing mast cell degranulation. It could thereby contribute to relieving allergy symptoms. However, the effect varies individually and may only appear after regular intake over a longer period. For optimal results, quercetin is often combined with vitamin C, which can improve bioavailability.
How long before the pollen season should I start taking natural remedies?
For optimal effect, it is recommended to start taking natural antiallergics about 4-6 weeks before the expected start of the pollen season relevant to you. This gives the active ingredients time to become active in the body and modulate the immune system before the actual pollen exposure begins.
Can children also take natural remedies for allergies?
Natural substances like quercetin, MSM, or probiotics could also be suitable for children with allergies, but in adjusted dosages. Before use in children, it is essential to consult a pediatric specialist, as not all supplements are equally suitable for all age groups and dosages must be individually adjusted.
Can I completely get rid of my allergy through dietary changes?
A complete cure of allergies solely through dietary changes is not scientifically proven. However, an anti-inflammatory, nutrient-rich diet could support the immune system and reduce the intensity of allergic reactions. In combination with other measures such as targeted intake of dietary supplements and reduction of allergen exposure, symptoms could be significantly alleviated.
Legal notice regarding health-related claims:
Our information is for general informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Dietary supplements do not replace a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. Health-related claims about dietary supplements must comply with the Health Claims Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 and be approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). If you have health complaints or questions, please consult a doctor.